Buying used hardware like CPUs or GPUs can sometimes be risky, as you may not know the exact condition of the components. Overclocking is a common practice where a component’s clock speed is pushed beyond its factory defaults to improve performance. However, this can sometimes reduce the hardware’s lifespan or lead to instability if done improperly. Thankfully, checking if a CPU or GPU is overclocked is straightforward. Below are three reliable methods to verify whether your hardware is overclocked.
Quick Links
1. Use CPU-Z to Check CPU Overclocking
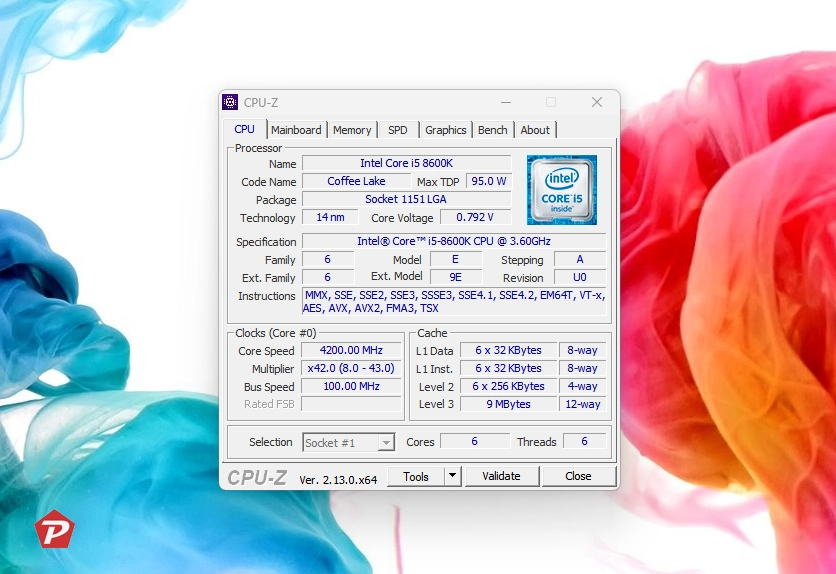
CPU-Z is one of the best tools to determine your CPU’s real-time clock speed. Overclocking a CPU involves boosting its clock speed beyond the default manufacturer settings, such as raising an Intel i9-10900K’s frequency from its stock maximum of 5.30GHz to a custom overclock of 6GHz.
Here’s how to use CPU-Z to check if your CPU is overclocked:
- Download and launch CPU-Z (free for Windows).
- Look under the Clocks section (bottom-left corner) for details like:
- Core Speed
- Multiplier
- Bus Frequency
- Perform an online search for your CPU’s stock clock speeds (e.g., “Intel i5-10600K maximum frequency”).
- Multiply the Bus Frequency by the highest multiplier value shown in parentheses in CPU-Z.
For instance:
- If the Bus Speed is 100MHz and the highest Multiplier is 48, the calculated clock speed would be 100 × 48 = 4800MHz or 4.8GHz.
- Compare this result to the stock specifications. If your calculated clock speed is higher, your CPU is overclocked.
2. Use GPU-Z to Check GPU Overclocking
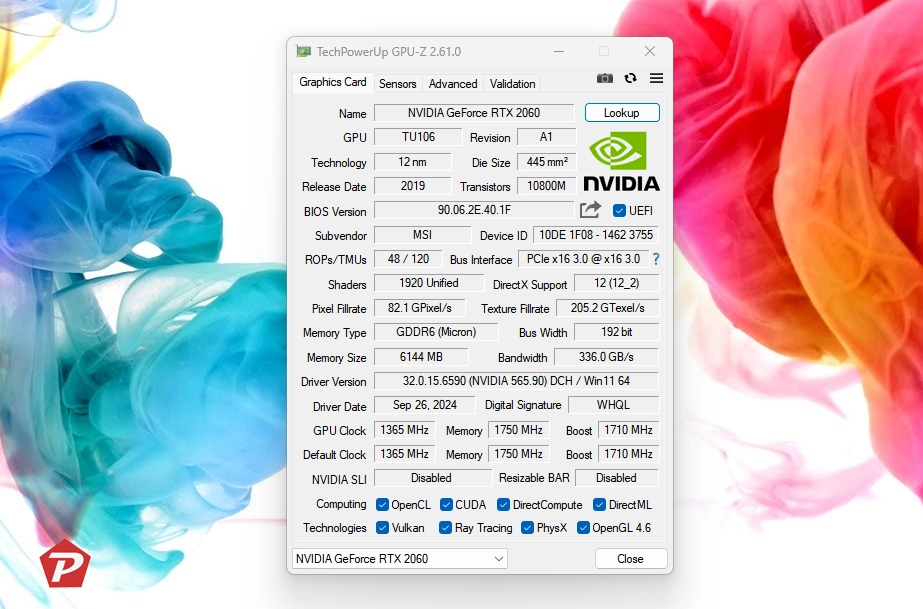
To check GPU overclocking, TechPowerUp’s GPU-Z is an excellent tool. It allows you to compare your GPU’s actual clock speeds with the manufacturer-provided stock values.
Here’s how to use GPU-Z to verify GPU overclocking:
- Download and open GPU-Z (free for Windows).
- Look for two key rows:
- Default Clock: The manufacturer’s base and boost clock speeds.
- GPU Clock: Your GPU’s current base and boost clock speeds.
- Compare the GPU Clock with the Default Clock:
- If the current GPU Clock exceeds the Default Clock, your GPU is overclocked.
For example:
- An Nvidia GeForce RTX 3080 with a Default Clock of 1440MHz and Boost of 1800MHz should display these same values in the GPU Clock section if running at stock speeds. If the GPU Clock exceeds these values, it’s overclocked.
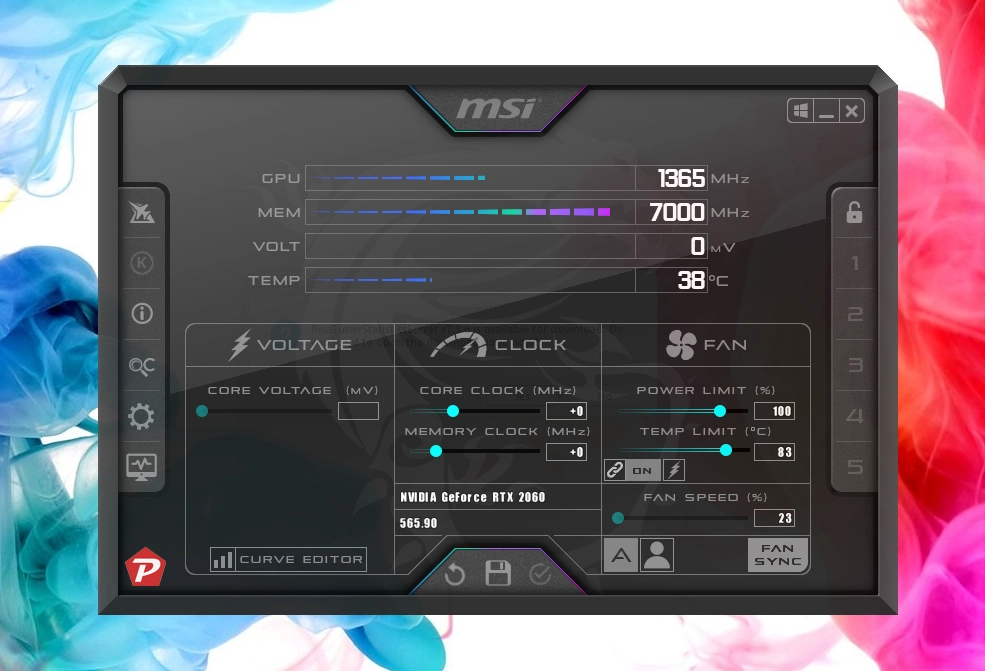
3. Use MSI Afterburner to Check and Manage GPU Overclocking
MSI Afterburner is widely regarded as one of the best tools for GPU overclocking and monitoring. It provides real-time data on your GPU’s clock speed, temperature, and fan performance.
Here’s how to check if your GPU is overclocked using MSI Afterburner:
- Install and launch MSI Afterburner (free for Windows).
- Look under the Clock section for two key values:
- Core Clock
- Memory Clock
- Check if the values display +0 or any positive number:
- A +0 value means the clocks are running at stock speeds.
- Positive values like +100 indicate overclocking has been applied.
Important Notes:
- Modern GPUs can overclock themselves dynamically based on the cooling setup and workload, so small variations in clock speeds are normal.
- Compare relative differences rather than expecting exact matches to online specifications.
Why It’s Important to Check for Overclocking
Knowing whether your CPU or GPU is overclocked helps you decide if you should maintain the current settings or revert to stock configurations. Overclocking can boost performance, especially for gaming or demanding workloads, but it carries risks such as overheating or hardware damage.
By using tools like CPU-Z, GPU-Z, and MSI Afterburner, you can easily detect overclocked hardware and ensure it’s running safely and efficiently.
Downloads:
- CPU-Z for Windows (Free)
- GPU-Z for Windows (Free)
- MSI Afterburner for Windows (Free)
Final Thoughts
If you find your hardware overclocked, ensure you have a proper cooling solution to handle the increased performance. Safe overclocking can offer a free performance boost, but if you’re unsure about the risks, sticking to stock settings might be the better choice.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read our Affiliate Policy.