Ethernet cables are the unsung heroes of our digital lives. They silently connect our devices to the internet, allowing us to stream, game, work, and connect with the world. However, not all Ethernet cables are created equal, and understanding the differences between them is essential for optimizing your network’s performance.
Quick Links
Ethernet Cables: An Overview
Ethernet cables are the physical channels that transmit data from your device to a router or modem. They come in various categories, each with its unique characteristics, designed for specific purposes.
Types of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables are a critical component of wired network connections. They come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and network speeds. Here are some of the most common types of Ethernet cables:
Cat5e Cables

Cat5e cables are among the older Ethernet cables but are still widely used. They support data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second) and are suitable for most home and small business networks.
Cat6 Cables
Cat6 cables are an improvement over Cat5e. They support higher data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances and offer better overall performance. Cat6 cables are commonly used in modern home networks and small to medium-sized businesses.
Cat6a Cables
Cat6a cables are an enhanced version of Cat6, providing even faster data transfer speeds and improved performance in high-interference environments. They can support data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances than Cat6 cables, making them suitable for larger networks and data centers.
Cat7 Cables
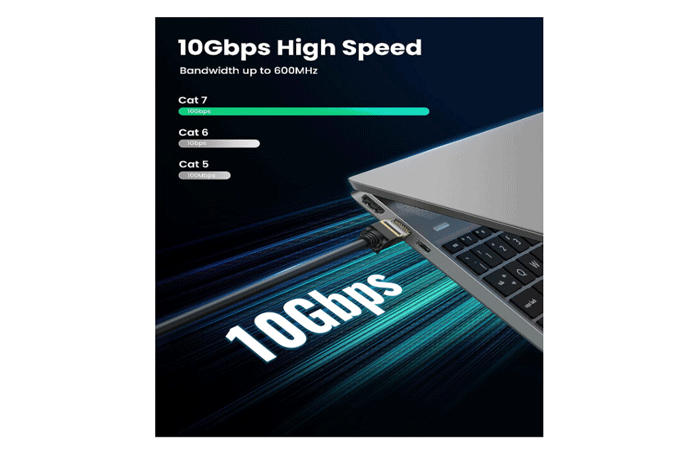
Cat7 cables are designed for even higher data transfer speeds, reaching up to 10 Gbps. They are shielded, which helps reduce interference and crosstalk, making them suitable for demanding applications and environments where electromagnetic interference is a concern.
Cat8 Cables
Cat8 cables are the most advanced standard Ethernet cables available. They can support data transfer speeds of up to 25 or 40 Gbps, depending on the version. Cat8 cables are typically used in data centers and high-speed networking environments.
It’s essential to choose the right type of Ethernet cable based on your network requirements, including data transfer speed, distance, and environmental factors. Upgrading to a higher category of cable can improve network performance and future-proof your infrastructure, but it’s also important to ensure that your network devices and equipment support the same or higher speeds as the cable you choose.
Ethernet Cable Connectors
RJ-45

RJ-45 connectors are the standard plugs for Ethernet cables. They feature eight pins and are used in most Ethernet applications.
Ethernet Jacks
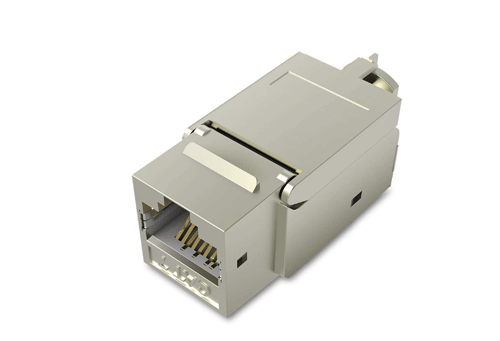
Ethernet jacks are the female counterparts to RJ-45 connectors, found on devices like computers, routers, and switches.
Ethernet Cable Uses
Ethernet cables are commonly used for connecting devices to the internet, but they also serve other purposes, including connecting devices within a local network and powering devices through Power over Ethernet (PoE).
Ethernet Cable Performance Factors
Speed
The speed of an Ethernet cable is determined by its category. Higher categories support faster data transfer rates.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over the cable. Higher bandwidth cables can handle more data at once.
Crosstalk
Crosstalk occurs when signals on one wire interfere with signals on adjacent wires. Better cables have reduced crosstalk.
Shielding
Shielding protects the cable from electromagnetic interference, ensuring a stable connection.
Selecting the Right Ethernet Cable
Choosing the right Ethernet cable depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like speed requirements, cable length, and the environment in which it will be used.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance of Ethernet cables are crucial for a reliable network. Avoid sharp bends and keep cables away from sources of interference.
Ethernet Cables vs. Wi-Fi
Ethernet cables offer a more stable and faster connection compared to Wi-Fi, making them the preferred choice for gaming and streaming.
Ethernet cables offer reliable, high-speed, and secure connections, ideal for activities like gaming and large file transfers. They have low latency and no wireless congestion. However, installing them can be complex.
In contrast, Wi-Fi provides convenience and mobility but is susceptible to signal interference and may have security concerns. It’s cost-effective initially and scalable, making it suitable for smaller setups. Choosing between Ethernet and Wi-Fi depends on specific needs, with many environments employing a combination of both to balance reliability and convenience.
Future of Ethernet Cables
As technology continues to advance, Ethernet cables are likely to evolve further, offering even faster speeds and better performance.
Conclusion
In the world of Ethernet cables, choosing the right one is essential to optimize your network’s performance. Whether you’re a casual internet user or a professional network administrator, understanding the differences between Ethernet cable types can make a significant difference in your online experience.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read our Affiliate Policy.