To troubleshoot problems on your Windows 7, 8, 8.1, 10, or 11 computer, accessing Safe Mode is crucial. Safe Mode helps you identify and fix issues caused by problematic software or drivers. It’s an essential diagnostic tool that loads only the most necessary components, allowing you to pinpoint and resolve issues without interference from unnecessary programs. Learning how to start or boot Windows in Safe Mode is a valuable skill that can aid in maintaining a smooth and trouble-free computing experience.
Quick Links
What Is Use Of Windows Safe Mode?
1. Diagnosing Software Issues:
Safe Mode is a powerful tool for troubleshooting software problems. It allows your system to start with only essential drivers and services, making it easier to identify and fix issues caused by incompatible or malfunctioning software.
2. Resolving Blue Screen of Death (BSOD):
If you’ve encountered the dreaded BSOD, entering Safe Mode can be a game-changer. By starting your system with minimal drivers, Safe Mode helps pinpoint the source of the problem, enabling you to take corrective measures.
3. Dealing with Unresponsive Applications:
When applications refuse to cooperate, Safe Mode comes to the rescue. By isolating the startup programs, it helps determine whether a third-party application is causing the trouble, allowing you to uninstall or update as needed.
4. Removing Malware:
Safe Mode is a valuable ally in the fight against malware. Booting your computer in Safe Mode prevents unnecessary applications from running, making it easier to detect and eliminate malicious software that may be hampering your system.
5. Updating Drivers Safely:
Updating drivers is crucial for system stability, but it can sometimes lead to compatibility issues. Safe Mode provides a secure environment for updating drivers without interference from other applications, reducing the risk of conflicts.
6. Identifying and Fixing Hardware Problems:
Safe Mode isn’t just for software troubleshooting. It’s also an excellent tool for diagnosing hardware issues. By starting your system with basic drivers, it helps determine whether hardware components are causing performance issues.
7. Basic Display Settings Adjustment:
If you’re having trouble with your display settings, Safe Mode allows you to start your computer with the most basic graphics drivers. This can be particularly useful if you need to troubleshoot display-related problems or driver conflicts.
8. Limited Device Drivers for Stability:
Safe Mode loads only essential device drivers, ensuring a stable environment. This is particularly useful when you need to perform critical tasks, such as data backup or system restoration, without the interference of unnecessary drivers.
9. Network Connectivity for Online Troubleshooting:
Contrary to common belief, Safe Mode does provide basic network connectivity. This feature is beneficial when you need to troubleshoot and fix issues related to internet connectivity or online applications.
10. Performing System Restore:
Safe Mode is the go-to choice when you need to perform a system restore. Starting your computer in Safe Mode ensures that the restore process occurs in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of interference from third-party applications.
11. Undoing Recent Changes:
Whether it’s a recent driver update or a system configuration change gone wrong, Safe Mode allows you to revert to a previous state. This undo feature is crucial for correcting mistakes without risking further complications.
12. Preventing System Freezes:
Safe Mode’s stripped-down functionality significantly reduces the chances of system freezes. It provides a clean slate for troubleshooting, helping you identify and address issues without the frustration of an unresponsive system.
13. Backing Up Important Data:
Before making significant changes or attempting complex troubleshooting, Safe Mode is the ideal environment for backing up crucial data. Its minimalistic approach ensures a smooth data transfer process without unnecessary application interference.
14. Regular System Checks:
Incorporating Safe Mode into your routine for regular system checks is a proactive approach to maintaining a healthy computer. It allows you to identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring optimal performance.
15. A Safe Haven for Troubleshooting Woes:
Ultimately, Safe Mode serves as a safe haven for users facing perplexing computer problems. Its unique features and capabilities make it an indispensable tool for both novice and experienced users alike.
By understanding the various use cases of Windows Safe Mode, you empower yourself to navigate and troubleshoot a wide range of issues effectively. Whether it’s software conflicts, hardware problems, or simply the need for a stable environment, Safe Mode is your key to a smoother computing experience.
Boot/Start Windows 7, 8, 8.1, 10 & 11 In Safe Mode
Simple Process To Start Windows in SafeMode –
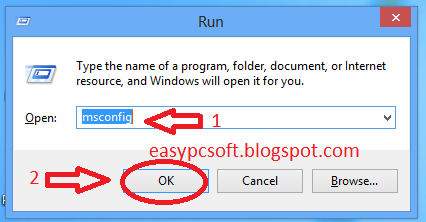
1- Press Windows Logo Key+R
2- Type in run command box msconfig & Click Ok.
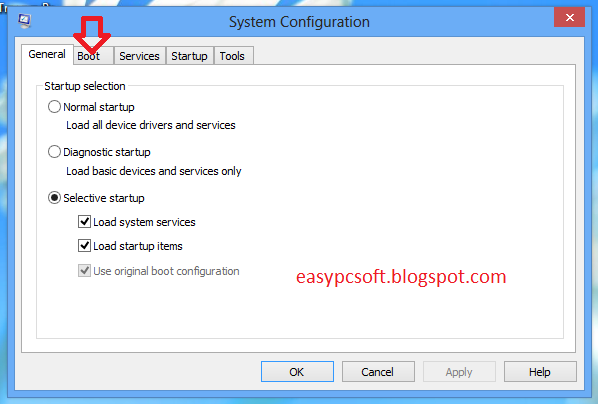
3-Click on Boot Tab.
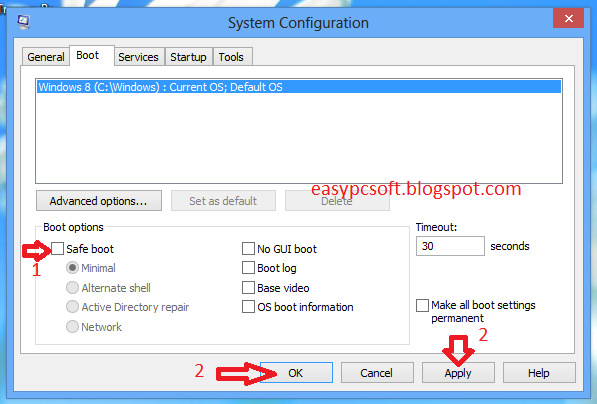
4- Click on Safe Boot Checkbox & Click Apply & Then Ok.
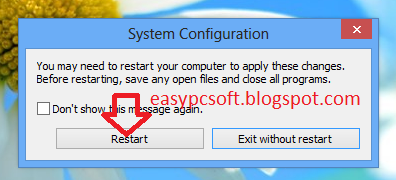
5- Click On Restart.
6- Windows Start in SafeMode.
7- If You want to Start In Normal Mode-
(1) Press Windows Logo + R
(2) type msconfig in Run command box
(3) Choose Normal startup radio button & Press Ok.
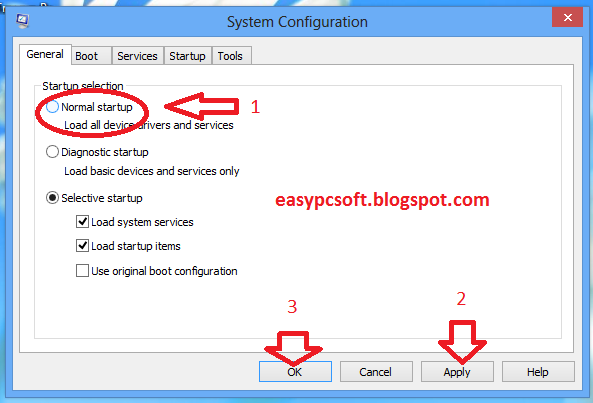
Note: If you don’t choose the “Normal startup” option while in safe mode, every time you restart your computer, Windows will keep loading in safe mode.
Boot/Start Windows in Normal Mode
1. Press Windows + R Key Together.
2. Windows run dialog box appears. Type in the box “msconfig” without quotes & Click on OK.
3. Now in General tab Startup selection Choose “Normal startup” radio button & Click on Apply & OK.
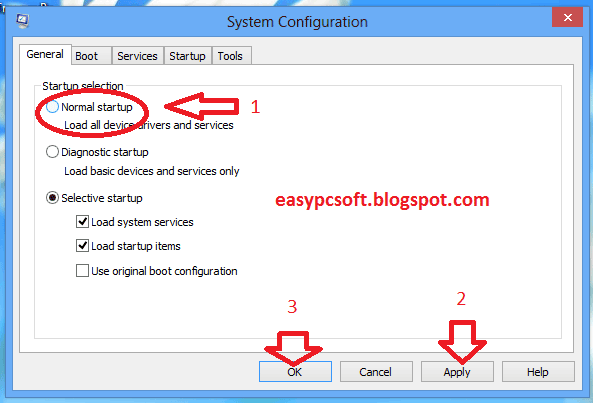
5. Now Click on Restart.
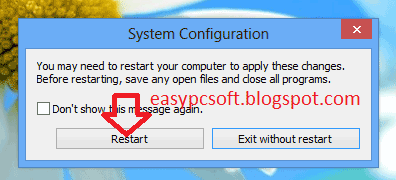
Now the Windows will Start again in Normal Mode.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read our Affiliate Policy.





