In our digital world, online privacy is more important than ever. Many people rely on Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to browse securely and unlock geo-blocked content. But let’s be real—VPNs have their downsides. They can slow down your internet speed, be pricey, and sometimes don’t live up to the hype. If you’re over the usual VPN headaches, it’s worth checking out some alternatives that might fit your needs better. Let’s dive into five VPN alternatives that could better suit your needs.
Quick Links
What is a VPN and Why Consider Alternatives?

Image Credit: Pixabay.com
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address by routing it through a server in a different location. While this is great for privacy, it’s not always the best fit for everyone.
Downsides of Using VPNs
- Reduced internet speed due to encryption.
- Higher costs for quality VPN services.
- Some websites block VPN traffic.
- Can be complex to configure for non-tech-savvy users.
Benefits of Exploring Alternatives
By looking beyond VPNs, you can discover solutions that offer faster speeds, lower costs, and more flexibility—all while maintaining online privacy.
5 Secure Alternatives to VPNs You Can Use in 2025
1. Try Smart DNS
Smart DNS is a simple yet effective way to access geo-restricted content without sacrificing speed. Unlike VPNs, Smart DNS doesn’t encrypt your traffic; instead, it reroutes your DNS queries through its servers.
How Smart DNS Works
Smart DNS changes your device’s DNS settings to its own, allowing you to access blocked websites as if you were in a different location. This makes it ideal for streaming and accessing restricted sites.
Benefits of Using Smart DNS
- Faster speeds due to no encryption.
- Ideal for streaming and gaming.
- Simple to set up on various devices.
Drawbacks of Smart DNS
- No IP masking, meaning your real IP is visible.
- Lacks encryption, which reduces security.
How to Set Up Smart DNS
- Choose a Smart DNS provider like Unlocator or Smart DNS Proxy.
- Sign up and get DNS addresses from the provider.
- Access your device’s DNS settings (usually found in network settings).
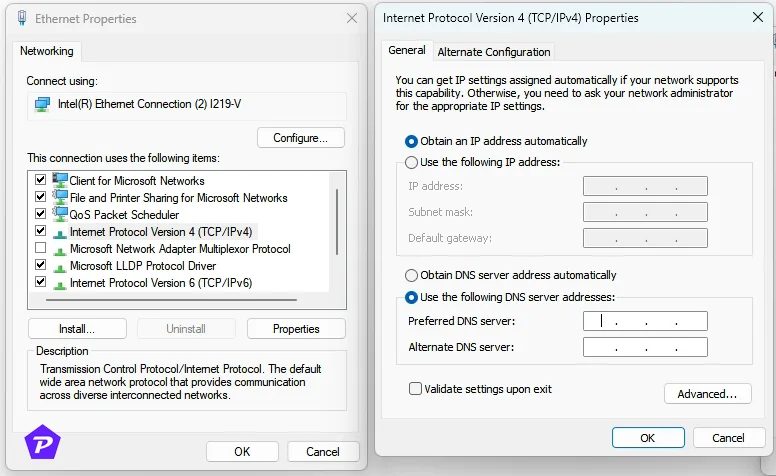
- Enter the provided DNS addresses.
- Restart your device to apply changes.
2. Route Your Traffic Through a Proxy Server
A proxy server acts as a middleman between you and the internet. It hides your IP address by routing your traffic through its IP address, making your online actions less traceable.
Types of Proxy Servers
- HTTP Proxy: Good for web browsing.
- HTTPS Proxy: Adds encryption for secure browsing.
- SOCKS Proxy: Versatile but slower.
Advantages of Proxy Servers
- Can be cost-effective, with many free options available.
- Helps in bypassing geo-restrictions.
- Useful for anonymous browsing.
Disadvantages of Using Proxies
- Many free proxies are slow and unreliable.
- Lack of encryption makes them less secure.
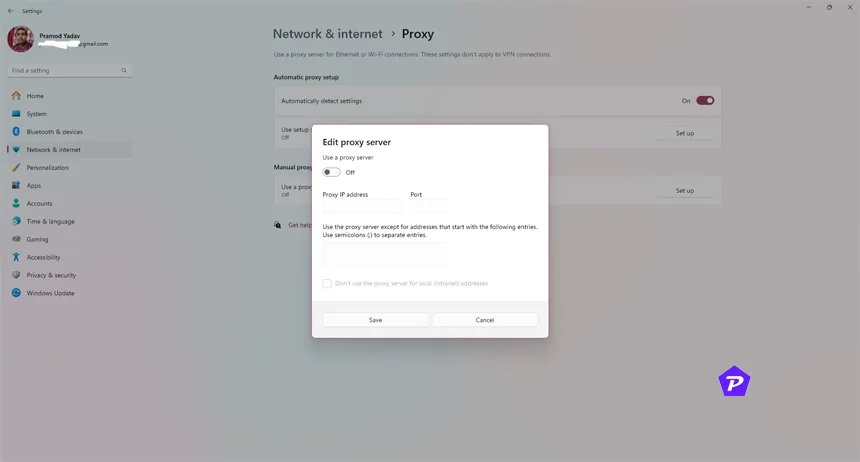
Setting Up a Proxy Server
- Choose a proxy server provider like Tuxler Proxy or KProxy.
- Configure your browser or device settings to use the proxy.
- Enter the proxy’s IP address and port number.
- Save settings and start browsing through the proxy.
You May Also Like:
3. Browsing With Tor
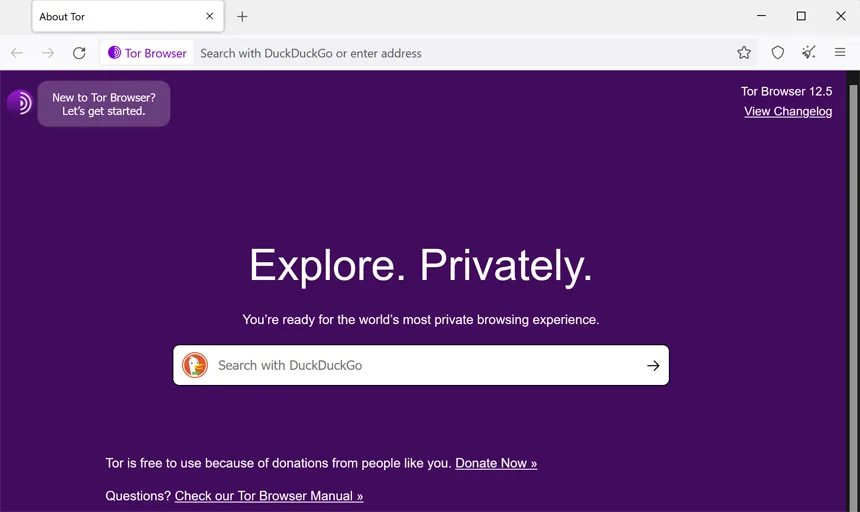
Tor, short for “The Onion Router,” is all about anonymity. It routes your traffic through multiple volunteer-operated servers, encrypting it at every step, which makes it incredibly hard to trace.
How Tor Works for Anonymous Browsing
Tor works like an onion, with your data passing through several encrypted layers before reaching its destination. This makes tracking your online activity nearly impossible.
Pros of Using Tor
- High level of anonymity.
- Free to use.
- Ideal for browsing sensitive content.
Cons and Limitations of Tor
- Slower browsing speeds.
- Not ideal for streaming or gaming.
- Some websites block Tor traffic.
Tips for Using Tor Safely
- Download the Tor Browser from the official website.
- Avoid installing plugins that could compromise your anonymity.
- Do not tweak the default settings unless you know what you’re doing.
- Use Tor bridges if your ISP blocks Tor access.
4. Use Remote Desktop
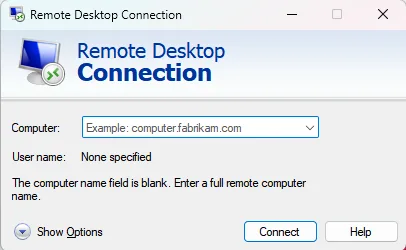
Remote desktop solutions allow you to control a computer in another location, letting you access region-specific content using a virtual machine (VM) in that location.
How Remote Desktops Work
By renting a VM from providers like AWS or Google Cloud, you can browse as if you were in that VM’s location. It’s like having a computer in another country without leaving your home.
Pros of Using Remote Desktops
- Access geo-restricted content with ease.
- High level of privacy.
- Flexible for different needs.
Cons to Keep in Mind
- Requires technical setup.
- Maintenance can be time-consuming.
- Costs can add up if using cloud providers.
Setting Up a Remote Desktop Connection
- Choose a cloud provider (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud).
- Create a VM in the desired location.
- Install remote desktop software (e.g., Microsoft Remote Desktop, TeamViewer).
- Connect to the VM using the software.
- Secure the VM with strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
5. Use SSH Tunneling
SSH (Secure Shell) tunneling allows you to create a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server. It’s a favored method for tech-savvy users who want robust security.
How SSH Works for Secure Browsing
An SSH tunnel encrypts all your traffic through a secure channel, providing an extra layer of privacy similar to a VPN.
Benefits of Using SSH Tunnels
- Strong encryption.
- IP masking capabilities.
- Useful for accessing remote services securely.
Challenges and Limitations
- Complex to set up for beginners.
- Requires access to a remote server.
- Slower speeds compared to unencrypted browsing.
Setting Up an SSH Tunnel
- Choose an SSH client (like PuTTY for Windows or Terminal for macOS/Linux).
- Access a remote server (you’ll need login credentials).
- Enter the command to initiate the SSH tunnel.
- Configure your browser to route traffic through the tunnel.
- Test the connection to ensure it’s secure.
Comparing VPN Alternatives: Which One is Right for You?
Speed Comparison
- Smart DNS: Fastest, no encryption.
- Proxies: Faster than VPNs, slower than Smart DNS.
- Tor: Slowest due to multi-layer encryption.
Privacy and Security
- Tor and SSH offer the highest anonymity.
- Smart DNS offers minimal privacy.
- Proxies vary depending on type and provider.
Cost Considerations
- Smart DNS and Proxies often have free options.
- Remote Desktops can be expensive for frequent use.
Ease of Use
- Smart DNS: Easiest to set up.
- Tor: Simple installation but slow.
- SSH and Remote Desktop: More complex, better for advanced users.
Conclusion
While VPNs remain a popular choice, they’re not the only way to secure your internet experience. Whether you’re looking for speed, flexibility, or a budget-friendly option, alternatives like Smart DNS, proxy servers, Tor, remote desktops, and SSH tunneling offer unique benefits. Choose the method that best aligns with your needs and enjoy a safer, more private browsing experience.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read our Affiliate Policy.





